Orthotopic Model
In Vivo Services
Orthotopic Model Overview
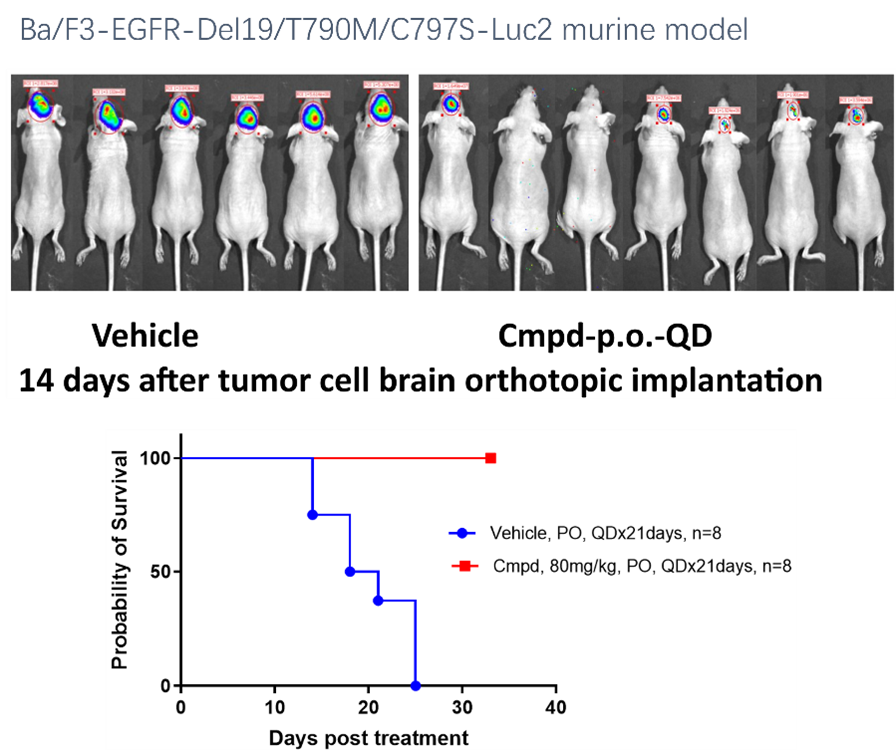
In orthotopic tumor models, tumor cells are implanted into the corresponding organ from which the tumor originates. In contrast, standard subcutaneous models involve implanting tumor cells under the skin, typically on the animal’s flank. Orthotopic tumor models hold greater clinical relevance compared to their subcutaneous counterparts as they establish an organ-specific tumor microenvironment that may vary in each cancer type. The orthotopic tumor implantation method allows researchers to more accurately observe cancer progression and assess drug efficacy. KYINNO has established various orthotopic models, including the engraftment of breast cells into the mammary fat pad and the implantation of luciferase-labeled tumor cells into the brain.
All in vivo Services
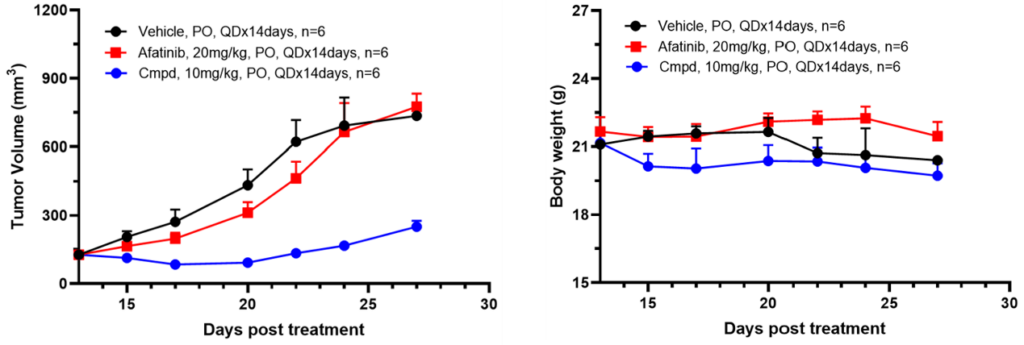
Ba/F3 Xenograft focuses on protein kinases, a cornerstone in cancer research. With FDA’s acknowledgment of kinase drugs, it offers important oncology insights aiding for deeper understanding.
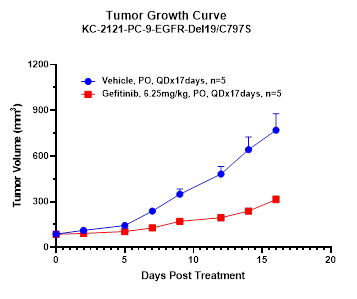
Gene-edited xenografts, utilizing tools like CRISPR/Cas9, offer precise modifications to tumor cell genomes, significantly expanding the horizons and potential of modern oncological research methodologies and insights.
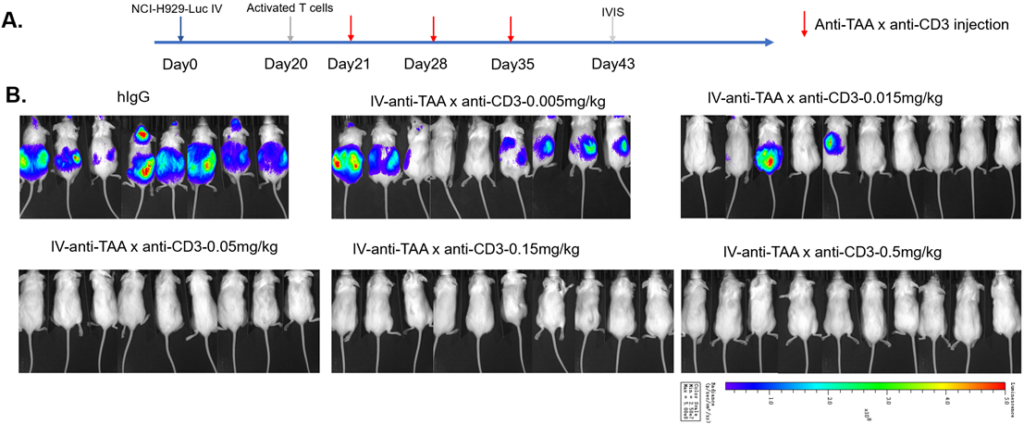
Luciferase tumor model provides insights into tumor growth and immune dynamics. Using bioluminescence, it provides real-time insights. This innovative approach deepens comprehension, advancing cancer research and promoting novel therapeutic discoveries.
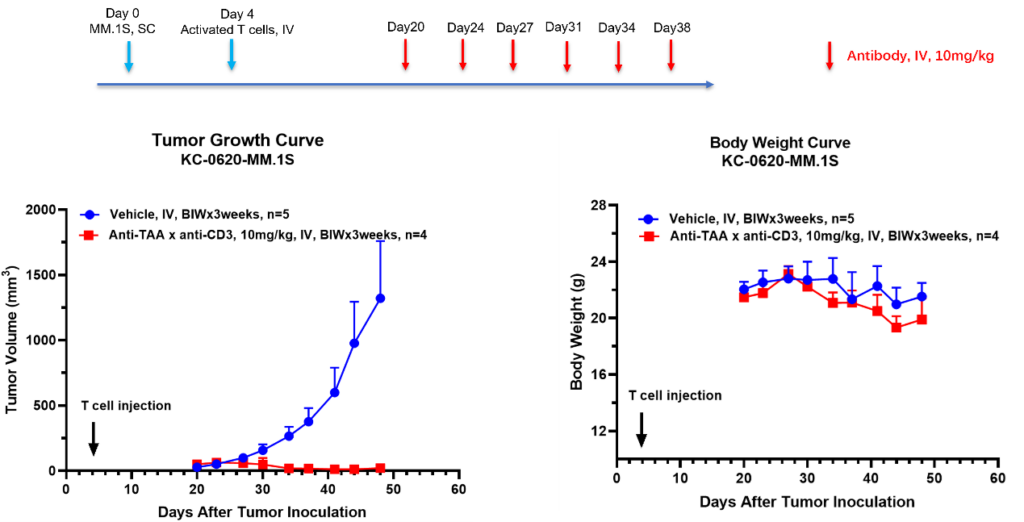
PBMC Humanized Mouse Model incorporates human T cells’ behavior, enabling detailed tumor immunology analysis. It presents a unique avenue for in-depth exploration, enriching research and offering a comprehensive study platform.
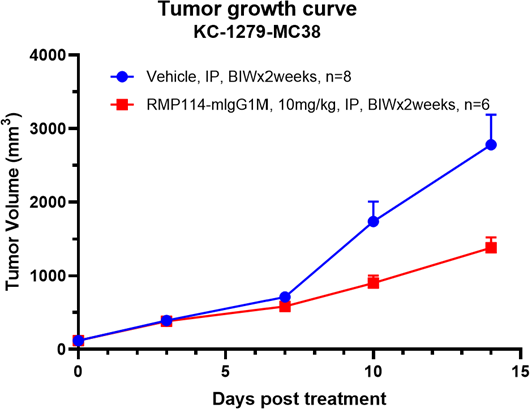
The Syngeneic Model leverages the uses of mouse-derived tumor tissues, placed into genetically similar hosts, contributing to consistency and depth in cancer studies. Ensures a genuine environment for cancer study.

The Subcutaneous tumor models are a leading choice for evaluating anti-cancer drug efficacy, supporting clinical trials, and understanding potential treatments. Its established method is a key component in therapeutic research.
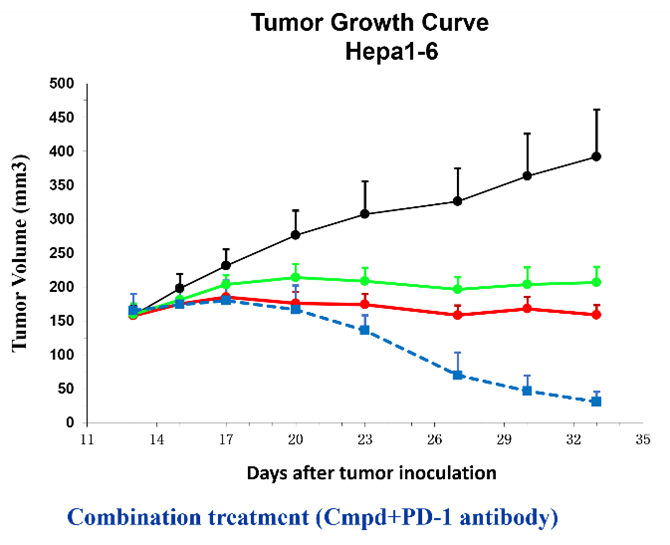
The subcutaneous tumor model is one of the most commonly used in vivo evaluation systems for assessing the efficacy of novel anti-cancer drugs. Typically, tumor …
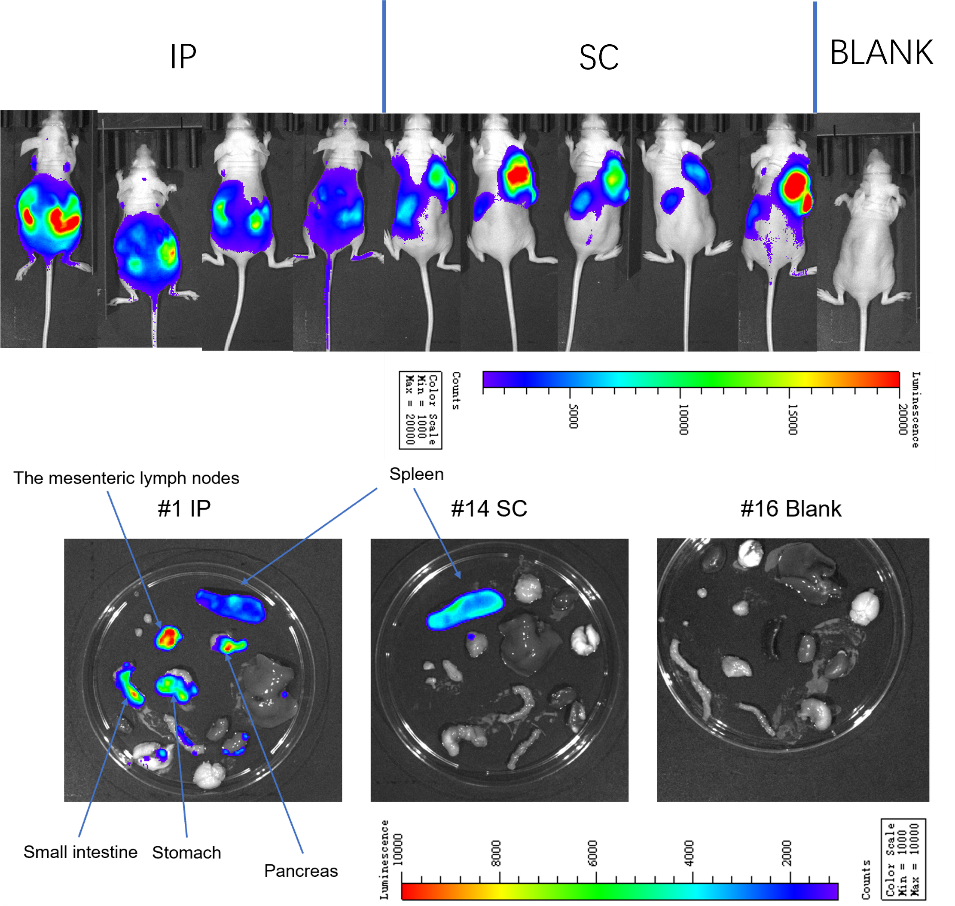
In cancer research, metastasis models are crucial tools that help us understand how tumors migrate from their original location to other parts of the body. Ba/F3 cells are a common type of tumor cell, especially in mouse models, where they exhibit metastasis.