Cell Proliferation Assay
In Vitro Services
Cell Proliferation Assay Overview
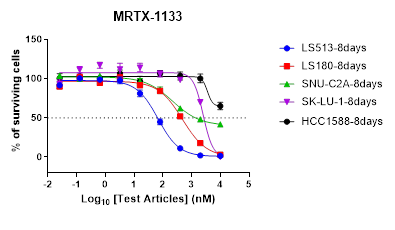
Cell viability and cell proliferation assays are essential components of any tumor inhibitor development program. Cell proliferation assays are widely employed for the initial assessment of the therapeutic effects of antineoplastic agents. The most commonly used method for cell proliferation assays is the 2D cell proliferation assay. In this assay, tumor cells are cultured either in suspension in a culture medium or as monolayers in cell culture plates. After treatment with compounds, cell viability is measured using the CTG reagent at the end of the experiment. Due to the simplicity of the experimental procedure, this standardized assay allows for the rapid testing of a large number of compounds simultaneously, and the 3D cell proliferation assay can also be integrated into this standard procedure.
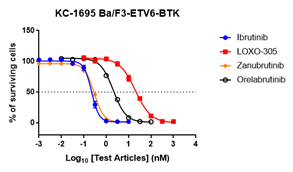
We possess the largest BaF3 engineered cell bank globally, enabling us to conduct rapid, high-throughput screening of compounds across a wide panel of cell lines. In our standard experiments, the drug incubation period extends up to 3 days, which can be extended to a maximum of 14 days if required by the project. Additionally, 3D experiments are always a valuable option for studying organoids.
All in vitro Services
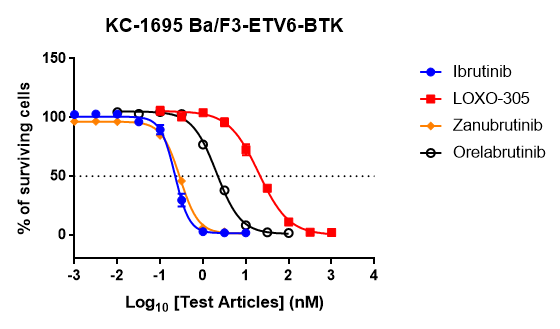
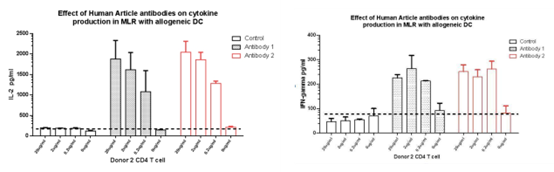
The 2D Cell Proliferation Assay, a primary method for cell growth studies, focuses on tumor cells cultured in suspension or monolayers. It allows for comprehensive analysis, highlighting cell development dynamics.
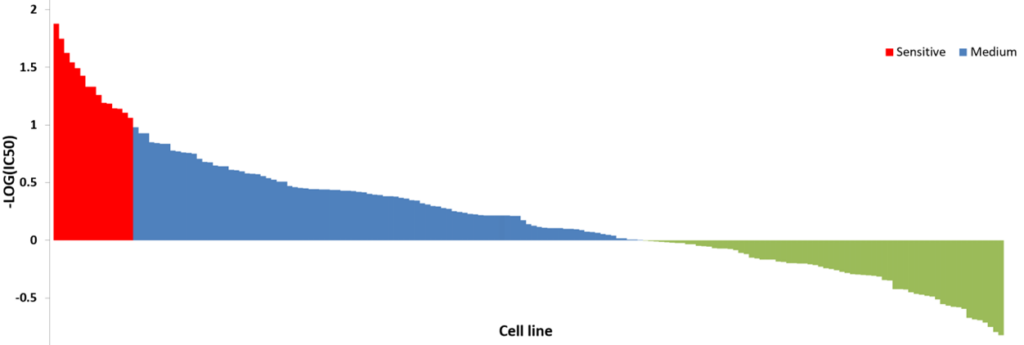
The value of tumor cell lines, as research models and drug discovery tools, is greatly enhanced when there is an understanding of the underlying genetic abnormalities that drive their phenotype. Kyinno provides customized cell panel studies to facilitate your drug discovery and biomarker programs.

Organoids, sophisticated 3D organ replicas grown in vitro, are vital in biomedical research, aiding disease modeling, drug testing, and understanding organ development. KYinno excels in cultivating organoids from diverse tumor tissues, collaborating closely with cancer hospitals to ensure translational relevance.

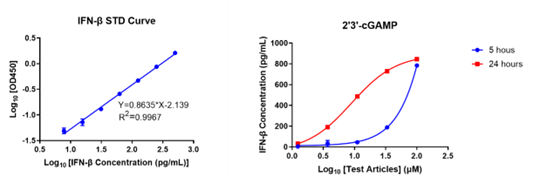
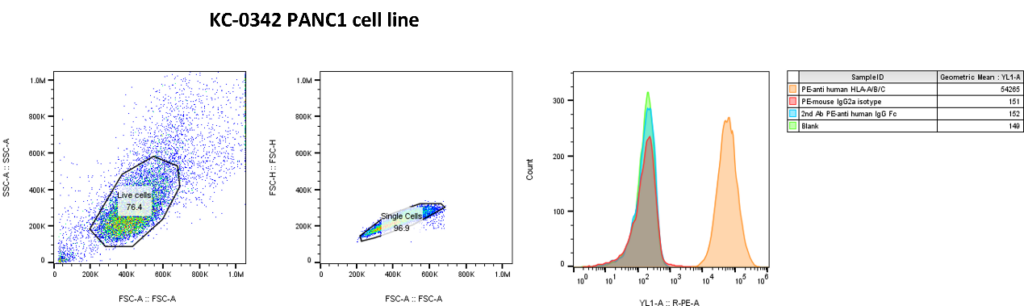
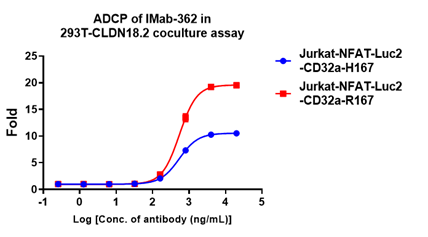
FACS Binding Assay or Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting, is a pivotal cellular biology research technique for binding evaluation. It offers insights into cellular binding mechanisms, enriching our understanding of cell interactions.